- The optical microscope, often referred to as the light microscope, is a type of microscope that uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small subjects.
- There are two basic types of optical microscopes:
- Simple microscopes
- Compound microscopes.
Simple Microscope
- A simple microscope is one which uses a single lens for magnification, such as a magnifying glass while a compound microscope uses several lenses to enhance the magnification of an object.
- A simple microscope uses a lens to enlarge an object through angular magnification alone, giving the viewer an erect enlarged virtual image.
- The use of a single convex lens or groups of lenses is found in simple magnification devices such as the magnifying glass, loupes, and eyepieces for telescopes and microscopes.
- A simple microscope is actually a convex lens of small focal length, which is used for seeing the magnified images of small objects.

Principle of Simple Microscope
A simple microscope works on the principle that when a tiny object is placed within its focus, a virtual, erect and magnified image of the object is formed at the least distance of distinct vision from the eye held close to the lens.
Magnification of Simple Microscope
The magnifying power of a simple microscope is given by:
M = 1 + D/F
Where, D = least distance of distinct vision
F = focal length of the convex lens
- The focal length of the convex lens should be small because smaller the focal length of the lens, greater will be its magnifying power.
- The maximum magnification of a simple microscope is about 10, which means that the object will appear 10 times larger by using the simple microscope of maximum magnification.
Instrumentation of Simple Microscope
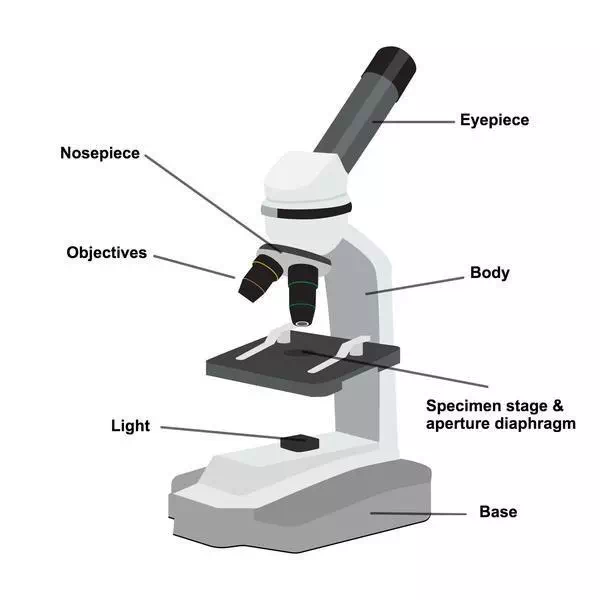
The parts of a simple microscope maybe:
(i) Mechanical parts
(ii) Optical parts
Mechanical parts:
These parts support the optical parts and help in their adjustment for focusing the object.
They include the following components:
- Metal Stand:
- It has a heavy base plate and a vertical rod fitted to it, which provide support and stability to other parts of the microscope.
- Stage:
- It is a rectangular metal plate fitted to the vertical rod.
- It has a central hole for light to pass from below.
- Slide with specimen to be observed is kept on the stage, in such a way that, the specimen remains just on the central hole.
- Some microscopes have a pair of slanting wings projecting from the both the sides of the stage. They provide support to hand for manipulating the object.
Optical parts:
These parts are involved in passing the light through the object (specimen) and magnifying its size.
The components of the optical parts are as follows:
- Mirror:
- A plano-convex mirror is fitted below the stage to the vertical rod by means of a frame.
- It focuses the surrounding light on the object to be observed.
- Lens:
- A biconvex lens is fitted above the stage, to the vertical rod, by means of a frame.
- It magnifies the size of the object and the enlarged virtual image formed is observed by keeping the eye above it.
- For proper focusing, the lens can be moved up and down by the frame.
Applications of Simple Microscope
- It is usually used for study of microscopic algae, fungi and biological specimen.
- The simple microscope is commonly used by watch makers to see the magnified view of small parts of a watch.
- It is also used by the jewelers to see the magnified view of the fine parts of jewellery.
- Simple microscope is used to see the enlarged image of letters of a book, textures of fibers or threads of a cloth.
- Simple microscope is used to see the magnified view of different particles of different types of soils.
- It is used by palmists to see enlarged view of the lines of our hand.
- Simple microscope is used by skin specialists to find out various diseases of skin.
- It is also used to see the details of stamp and engravings.