According to cell theory, cells are the main unit of organization in biology. Whether you are a single cell or a blue whale with trillions of cells, you are still made of cells. All cells are contained by a cell membrane that keeps the pieces inside. When you think about a membrane, imagine it is like a big plastic bag with some tiny holes. That bag holds all of the cell pieces and fluids inside the cell and keeps any nasty things outside the cell. The holes are there to let some things move in and out of the cell.
Flexible Containers

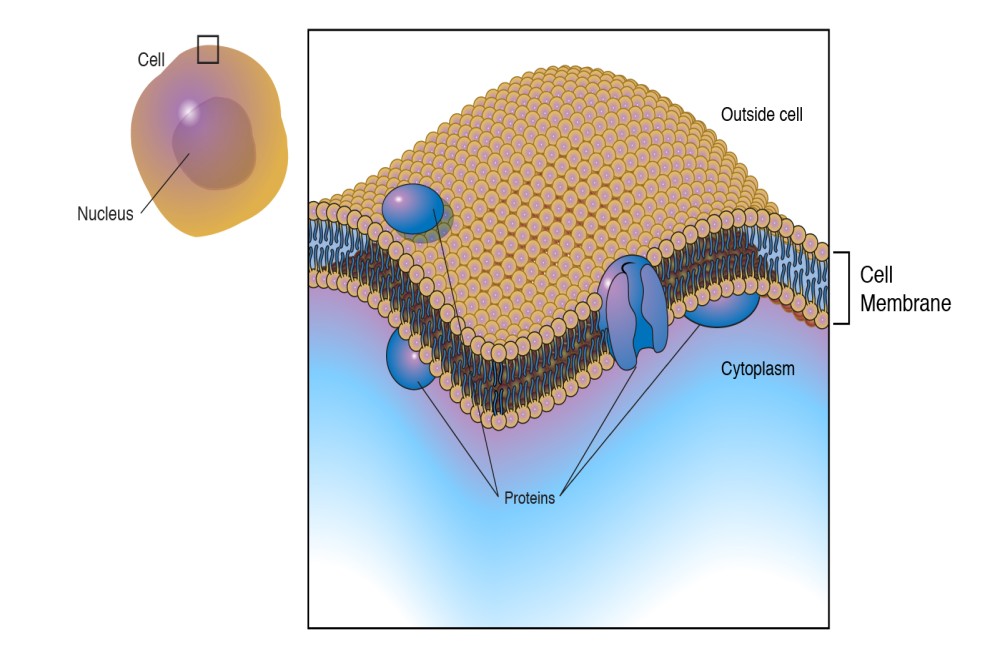
The cell membrane is not a solid structure. It is made of millions of smaller molecules that create a flexible and porous container. Proteins and phospholipids make up most of the membrane structure. The phospholipids make the basic bag. The proteins are found around the holes and help move molecules in and out of the cell. There are also proteins attached to the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane.
Scientists use the fluid mosaic model to describe the organization of phospholipids and proteins. The model shows you that phospholipid molecules are shaped with a head and a tail region. The head section of the molecule likes water (hydrophilic) while the tail does not (hydrophobic). Because the tails want to avoid water, they tend to stick to each other and let the heads face the watery (aqueous) areas inside and outside of the cell. The two surfaces of molecules create the lipid bilayer.
Ingrained in the Membrane
What about the membrane proteins? Scientists have shown that many proteins float in the lipid bilayer. Some are permanently attached while others are only attached temporarily. Some are only attached to the inner or outer layer of the membrane while the transmembrane proteins pass through the entire structure. The transmembrane proteins that cross the bilayer are very important in the active transport of ions and small molecules.
Different Membranes of the Cell
As you learn more about cell organelles, you will find that they all have a membrane. Organelle membranes do not have the same chemical makeup as the cell membrane. They have different lipids and proteins that make them unique. The membrane that surrounds a lysosome is different from the membrane around the endoplasmic reticulum.
Some organelles have two membranes. A mitochondrion has an outer and inner membrane. The outer membrane contains the mitochondrion parts. The inner membrane holds digestive enzymes that break down food. While we talk about membranes all the time, you should remember they all use a basic phospholipid bilayer structure, but you will find many variations throughout the cell.