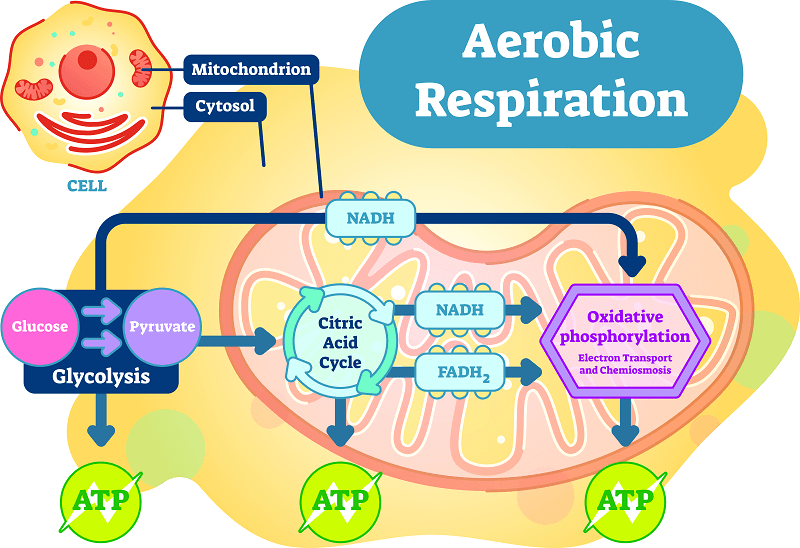
Certain prokaryotes, including some species of bacteria and Archaea, use anaerobic respiration. For example, the group of Archaea called methanogens reduces carbon dioxide to methane to oxidize NADH. These microorganisms are found in soil and in the digestive tracts of ruminants, such as cows and sheep. Similarly, sulfate-reducing bacteria and Archaea, most of which are anaerobic (Figure 4.23), reduce sulfate to hydrogen sulfide to regenerate NAD+ from NADH.

Figure 4.23 The green color seen in these coastal waters is from an eruption of hydrogen sulfide. Anaerobic, sulfate-reducing bacteria release hydrogen sulfide gas as they decompose algae in the water. (credit: NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Land Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC)
Other fermentation methods occur in bacteria. Many prokaryotes are facultatively anaerobic. This means that they can switch between aerobic respiration and fermentation, depending on the availability of oxygen. Certain prokaryotes, like Clostridia bacteria, are obligate anaerobes. Obligate anaerobes live and grow in the absence of molecular oxygen. Oxygen is a poison to these microorganisms and kills them upon exposure. It should be noted that all forms of fermentation, except lactic acid fermentation, produce gas. The production of particular types of gas is used as an indicator of the fermentation of specific carbohydrates, which plays a role in the laboratory identification of the bacteria. The various methods of fermentation are used by different organisms to ensure an adequate supply of NAD+ for the sixth step in glycolysis. Without these pathways, that step would not occur, and no ATP would be harvested from the breakdown of glucose.
If NADH cannot be metabolized through aerobic respiration, another electron acceptor is used. Most organisms will use some form of fermentation to accomplish the regeneration of NAD+, ensuring the continuation of glycolysis. The regeneration of NAD+ in fermentation is not accompanied by ATP production; therefore, the potential for NADH to produce ATP using an electron transport chain is not utilized.
Connections to Other Metabolic Pathways
You have learned about the catabolism of glucose, which provides energy to living cells. But living things consume more than just glucose for food. How does a turkey sandwich, which contains protein, provide energy to your cells? This happens because all of the catabolic pathways for carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids eventually connect into glycolysis and the citric acid cycle pathways (Figure 4.24). Metabolic pathways should be thought of as porous—that is, substances enter from other pathways, and other substances leave for other pathways. These pathways are not closed systems. Many of the products in a particular pathway are reactants in other pathways.
Connections of Other Sugars to Glucose Metabolism
Glycogen, a polymer of glucose, is a short-term energy storage molecule in animals. When there is adequate ATP present, excess glucose is converted into glycogen for storage. Glycogen is made and stored in the liver and muscle. Glycogen will be taken out of storage if blood sugar levels drop. The presence of glycogen in muscle cells as a source of glucose allows ATP to be produced for a longer time during exercise.
Sucrose is a disaccharide made from glucose and fructose bonded together. Sucrose is broken down in the small intestine, and the glucose and fructose are absorbed separately. Fructose is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose (which is part of milk sugar, the disaccharide lactose), that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. The catabolism of both fructose and galactose produces the same number of ATP molecules as glucose.
Connections of Proteins to Glucose Metabolism
Proteins are broken down by a variety of enzymes in cells. Most of the time, amino acids are recycled into new proteins. If there are excess amino acids, however, or if the body is in a state of famine, some amino acids will be shunted into pathways of glucose catabolism. Each amino acid must have its amino group removed prior to entry into these pathways. The amino group is converted into ammonia. In mammals, the liver synthesizes urea from two ammonia molecules and a carbon dioxide molecule. Thus, urea is the principal waste product in mammals from the nitrogen originating in amino acids, and it leaves the body in urine.
Connections of Lipids to Glucose Metabolism
The lipids that are connected to the glucose pathways are cholesterol and triglycerides. Cholesterol is a lipid that contributes to cell membrane flexibility and is a precursor of steroid hormones. The synthesis of cholesterol starts with acetyl CoA and proceeds in only one direction. The process cannot be reversed, and ATP is not produced.
Triglycerides are a form of long-term energy storage in animals. Triglycerides store about twice as much energy as carbohydrates. Triglycerides are made of glycerol and three fatty acids. Animals can make most of the fatty acids they need. Triglycerides can be both made and broken down through parts of the glucose catabolism pathways. Glycerol can be phosphorylated and proceeds through glycolysis. Fatty acids are broken into two-carbon units that enter the citric acid cycle.
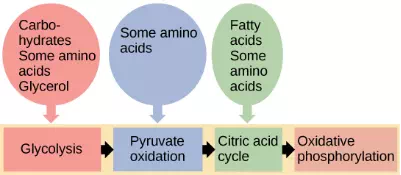
Figure 4.24 Glycogen from the liver and muscles, together with fats, can feed into the catabolic pathways for carbohydrates.
Pathways of Photosynthesis and Cellular Metabolism Photosynthesis and cellular metabolism consist of several very complex pathways. It is generally thought that the first cells arose in an aqueous environment—a “soup” of nutrients. If these cells reproduced successfully and their numbers climbed steadily, it follows that the cells would begin to deplete the nutrients from the medium in which they lived, as they shifted the nutrients into their own cells. This hypothetical situation would have resulted in natural selection favoring those organisms that could exist by using the nutrients that remained in their environment and by manipulating these nutrients into materials that they could use to survive. Additionally, selection would favor those organisms that could extract maximal value from the available nutrients.
An early form of photosynthesis developed that harnessed the sun’s energy using compounds other than water as a source of hydrogen atoms, but this pathway did not produce free oxygen. It is thought that glycolysis developed prior to this time and could take advantage of simple sugars being produced, but these reactions were not able to fully extract the energy stored in the carbohydrates. A later form of photosynthesis used water as a source of hydrogen ions and generated free oxygen. Over time, the atmosphere became oxygenated. Living things adapted to exploit this new atmosphere and allowed respiration as we know it to evolve. When the full process of photosynthesis as we know it developed and the atmosphere became oxygenated, cells were finally able to use the oxygen expelled by photosynthesis to extract more energy from the sugar molecules using the citric acid cycle.
The breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids connect with the pathways of glucose catabolism. The carbohydrates that can also feed into glucose catabolism include galactose, fructose, and glycogen. These connect with glycolysis. The amino acids from proteins connect with glucose catabolism through pyruvate, acetyl CoA, and components of the citric acid cycle. Cholesterol synthesis starts with acetyl CoA, and the components of triglycerides are picked up by acetyl CoA and enter the citric acid cycle.
Connections to Other Metabolic Pathways
You have learned about the catabolism of glucose, which provides energy to living cells. But living things consume more than just glucose for food. How does a turkey sandwich, which contains protein, provide energy to your cells? This happens because all of the catabolic pathways for carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids eventually connect into glycolysis and the citric acid cycle pathways (Figure 4.24). Metabolic pathways should be thought of as porous—that is, substances enter from other pathways, and other substances leave for other pathways. These pathways are not closed systems. Many of the products in a particular pathway are reactants in other pathways.
Connections of Other Sugars to Glucose Metabolism
Glycogen, a polymer of glucose, is a short-term energy storage molecule in animals. When there is adequate ATP present, excess glucose is converted into glycogen for storage. Glycogen is made and stored in the liver and muscle. Glycogen will be taken out of storage if blood sugar levels drop. The presence of glycogen in muscle cells as a source of glucose allows ATP to be produced for a longer time during exercise.
Sucrose is a disaccharide made from glucose and fructose bonded together. Sucrose is broken down in the small intestine, and the glucose and fructose are absorbed separately. Fructose is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose (which is part of milk sugar, the disaccharide lactose), that are absorbed directly into the bloodstream during digestion. The catabolism of both fructose and galactose produces the same number of ATP molecules as glucose.
Connections of Proteins to Glucose Metabolism
Proteins are broken down by a variety of enzymes in cells. Most of the time, amino acids are recycled into new proteins. If there are excess amino acids, however, or if the body is in a state of famine, some amino acids will be shunted into pathways of glucose catabolism. Each amino acid must have its amino group removed prior to entry into these pathways. The amino group is converted into ammonia. In mammals, the liver synthesizes urea from two ammonia molecules and a carbon dioxide molecule. Thus, urea is the principal waste product in mammals from the nitrogen originating in amino acids, and it leaves the body in urine.
Connections of Lipids to Glucose Metabolism
The lipids that are connected to the glucose pathways are cholesterol and triglycerides. Cholesterol is a lipid that contributes to cell membrane flexibility and is a precursor of steroid hormones. The synthesis of cholesterol starts with acetyl CoA and proceeds in only one direction. The process cannot be reversed, and ATP is not produced.
Triglycerides are a form of long-term energy storage in animals. Triglycerides store about twice as much energy as carbohydrates. Triglycerides are made of glycerol and three fatty acids. Animals can make most of the fatty acids they need. Triglycerides can be both made and broken down through parts of the glucose catabolism pathways. Glycerol can be phosphorylated and proceeds through glycolysis. Fatty acids are broken into two-carbon units that enter the citric acid cycle.

Figure 4.24 Glycogen from the liver and muscles, together with fats, can feed into the catabolic pathways for carbohydrates.
Pathways of Photosynthesis and Cellular Metabolism Photosynthesis and cellular metabolism consist of several very complex pathways. It is generally thought that the first cells arose in an aqueous environment—a “soup” of nutrients. If these cells reproduced successfully and their numbers climbed steadily, it follows that the cells would begin to deplete the nutrients from the medium in which they lived, as they shifted the nutrients into their own cells. This hypothetical situation would have resulted in natural selection favoring those organisms that could exist by using the nutrients that remained in their environment and by manipulating these nutrients into materials that they could use to survive. Additionally, selection would favor those organisms that could extract maximal value from the available nutrients.
An early form of photosynthesis developed that harnessed the sun’s energy using compounds other than water as a source of hydrogen atoms, but this pathway did not produce free oxygen. It is thought that glycolysis developed prior to this time and could take advantage of simple sugars being produced, but these reactions were not able to fully extract the energy stored in the carbohydrates. A later form of photosynthesis used water as a source of hydrogen ions and generated free oxygen. Over time, the atmosphere became oxygenated. Living things adapted to exploit this new atmosphere and allowed respiration as we know it to evolve. When the full process of photosynthesis as we know it developed and the atmosphere became oxygenated, cells were finally able to use the oxygen expelled by photosynthesis to extract more energy from the sugar molecules using the citric acid cycle.
The breakdown and synthesis of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids connect with the pathways of glucose catabolism. The carbohydrates that can also feed into glucose catabolism include galactose, fructose, and glycogen. These connect with glycolysis. The amino acids from proteins connect with glucose catabolism through pyruvate, acetyl CoA, and components of the citric acid cycle. Cholesterol synthesis starts with acetyl CoA, and the components of triglycerides are picked up by acetyl CoA and enter the citric acid cycle.