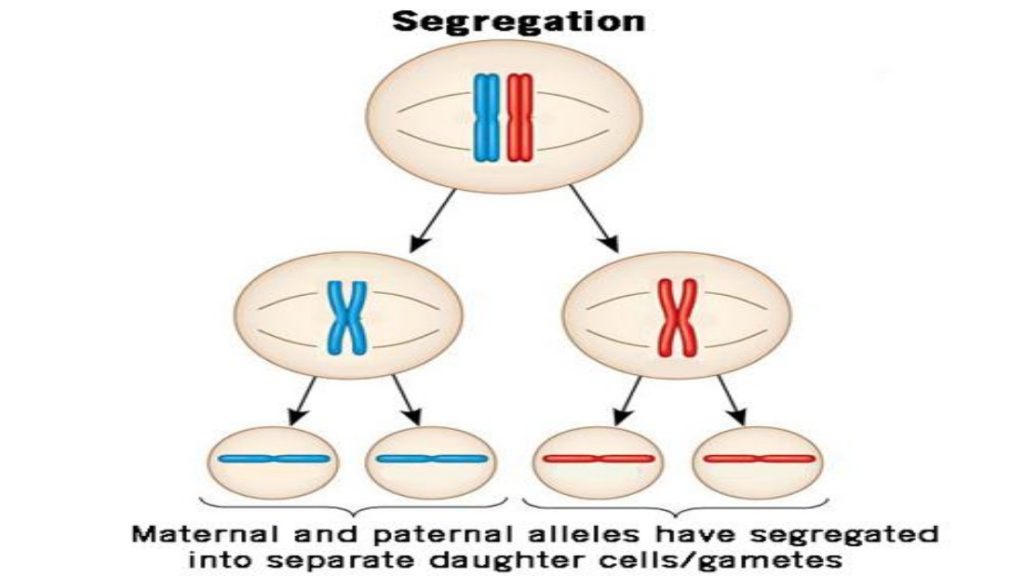
Observing that true-breeding pea plants with contrasting traits gave rise to F1 generations that all expressed the dominant trait and F2 generations that expressed the dominant and recessive traits in a 3:1 ratio, Mendel proposed the law of segregation. This law states that paired unit factors (genes) must segregate equally into gametes such that offspring have an equal likelihood of inheriting either factor. For the F2 generation of a monohybrid cross, the following three possible combinations of genotypes result: homozygous dominant, heterozygous, or homozygous recessive. Because heterozygotes could arise from two different pathways (receiving one dominant and one recessive allele from either parent), and because heterozygotes and homozygous dominant individuals are phenotypically identical, the law supports Mendel’s observed 3:1 phenotypic ratio. The equal segregation of alleles is the reason we can apply the Punnett square to accurately predict the offspring of parents with known genotypes. The physical basis of Mendel’s law of segregation is the first division of meiosis in which the homologous chromosomes with their different versions of each gene are segregated into daughter nuclei. This process was not understood by the scientific community during Mendel’s lifetime (Figure 8.7).
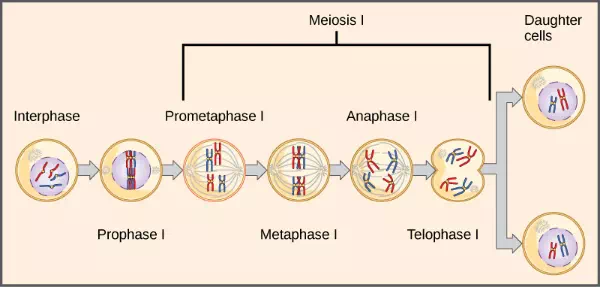
Figure 8.7 The first division in meiosis is shown.
Test Cross
Beyond predicting the offspring of a cross between known homozygous or heterozygous parents, Mendel also developed a way to determine whether an organism that expressed a dominant trait was a heterozygote or a homozygote. Called the test cross, this technique is still used by plant and animal breeders. In a test cross, the dominant-expressing organism is crossed with an organism that is homozygous recessive for the same characteristic. If the dominant-expressing organism is a homozygote, then all F1 offspring will be heterozygotes expressing the dominant trait (Figure 8.8). Alternatively, if the dominant-expressing organism is a heterozygote, the F1 offspring will exhibit a 1:1 ratio of heterozygotes and recessive homozygotes (Figure 8.9). The test cross further validates Mendel’s postulate that pairs of unit factors segregate equally.
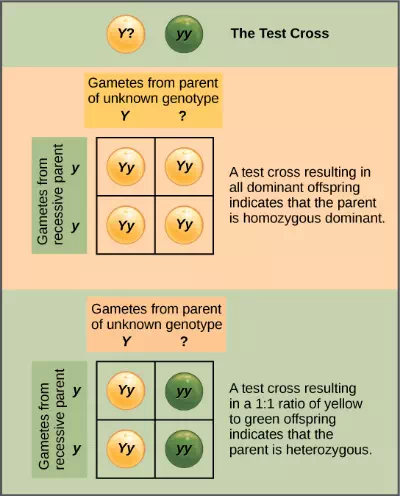
Figure 8.8 A test cross can be performed to determine whether an organism expressing a dominant trait is a homozygote or a heterozygote.
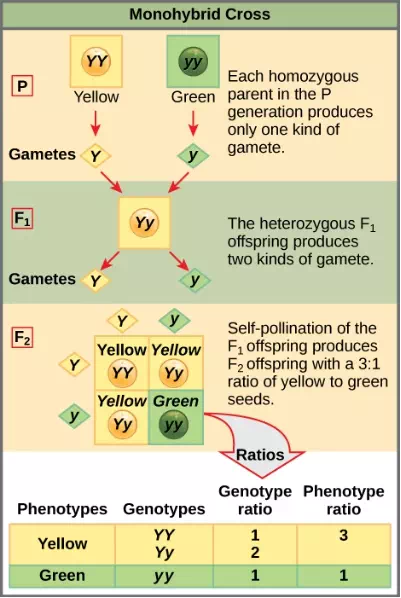
Figure 8.9 This Punnett square shows the cross between plants with yellow seeds and green seeds. The cross between the true-breeding P plants produces F1 heterozygotes that can be self-fertilized. The self-cross of the F1 generation can be analyzed with a Punnett square to predict the genotypes of the F2 generation. Given an inheritance pattern of dominant–recessive, the genotypic and phenotypic ratios can then be determined.
In pea plants, round peas (R) are dominant to wrinkled peas (r). You do a test cross between a pea plant with wrinkled peas (genotype rr) and a plant of unknown genotype that has round peas. You end up with three plants, all which have round peas. From this data, can you tell if the parent plant is homozygous dominant or heterozygous?
You cannot be sure if the plant is homozygous or heterozygous as the data set is too small: by random chance, all three plants might have acquired only the dominant gene even if the recessive one is present.