In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, the second function of DNA (the first was replication) is to provide the information needed to construct the proteins necessary so that the cell can perform all of its functions. To do this, the DNA is “read” or transcribed into an mRNA molecule. The mRNA then provides the code to form a protein by a process called translation. Through the processes of transcription and translation, a protein is built with a specific sequence of amino acids that was originally encoded in the DNA. This module discusses the details of transcription.
The Central Dogma: DNA Encodes RNA; RNA Encodes Protein
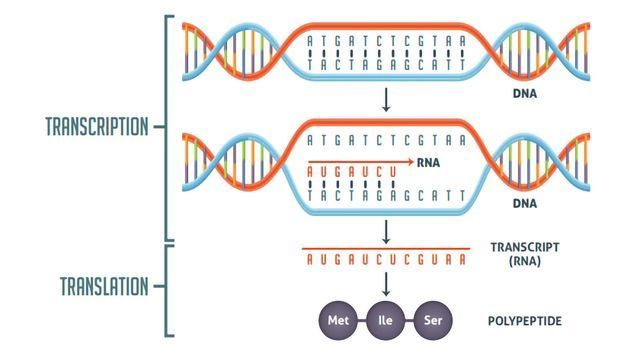
The flow of genetic information in cells from DNA to mRNA to protein is described by the central dogma (Figure 9.14), which states that genes specify the sequences of mRNAs, which in turn specify the sequences of proteins.
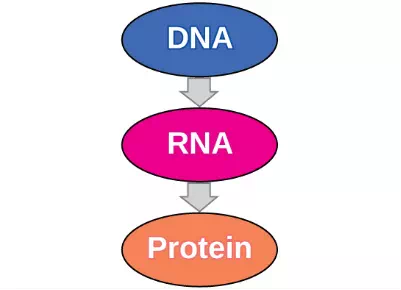
Figure 9.14 The central dogma states that DNA encodes RNA, which in turn encodes protein.
The copying of DNA to mRNA is relatively straightforward, with one nucleotide being added to the mRNA strand for every complementary nucleotide read in the DNA strand. The translation to protein is more complex because groups of three mRNA nucleotides correspond to one amino acid of the protein sequence. However, as we shall see in the next module, the translation to protein is still systematic, such that nucleotides 1 to 3 correspond to amino acid 1, nucleotides 4 to 6 correspond to amino acid 2, and so on.
Transcription: from DNA to mRNA
Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes perform fundamentally the same process of transcription, with the important difference of the membrane-bound nucleus in eukaryotes. With the genes bound in the nucleus, transcription occurs in the nucleus of the cell and the mRNA transcript must be transported to the cytoplasm. The prokaryotes, which include bacteria and archaea, lack membrane-bound nuclei and other organelles, and transcription occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, transcription occurs in three main stages: initiation, elongation, and termination.
Initiation
Transcription requires the DNA double helix to partially unwind in the region of mRNA synthesis. The region of unwinding is called a transcription bubble. The DNA sequence onto which the proteins and enzymes involved in transcription bind to initiate the process is called a promoter. In most cases, promoters exist upstream of the genes they regulate. The specific sequence of a promoter is very important because it determines whether the corresponding gene is transcribed all of the time, some of the time, or hardly at all (Figure 9.15).
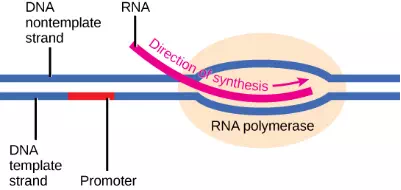
Figure 9.15 The initiation of transcription begins when DNA is unwound, forming a transcription bubble. Enzymes and other proteins involved in transcription bind at the promoter.
Elongation
Transcription always proceeds from one of the two DNA strands, which is called the template strand. The mRNA product is complementary to the template strand and is almost identical to the other DNA strand, called the nontemplate strand, with the exception that RNA contains a uracil (U) in place of the thymine (T) found in DNA. During elongation, an enzyme called RNA polymeraseproceeds along the DNA template adding nucleotides by base pairing with the DNA template in a manner similar to DNA replication, with the difference that an RNA strand is being synthesized that does not remain bound to the DNA template. As elongation proceeds, the DNA is continuously unwound ahead of the core enzyme and rewound behind it (Figure 9.16).
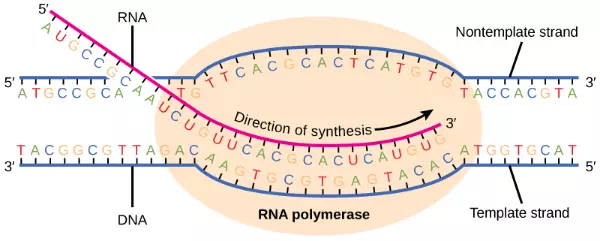
Figure 9.16 During elongation, RNA polymerase tracks along the DNA template, synthesizes mRNA in the 5′ to 3′ direction, and unwinds then rewinds the DNA as it is read.
Termination
Once a gene is transcribed, the prokaryotic polymerase needs to be instructed to dissociate from the DNA template and liberate the newly made mRNA. Depending on the gene being transcribed, there are two kinds of termination signals, but both involve repeated nucleotide sequences in the DNA template that result in RNA polymerase stalling, leaving the DNA template, and freeing the mRNA transcript.
On termination, the process of transcription is complete. In a prokaryotic cell, by the time termination occurs, the transcript would already have been used to partially synthesize numerous copies of the encoded protein because these processes can occur concurrently using multiple ribosomes (polyribosomes) (Figure 9.17). In contrast, the presence of a nucleus in eukaryotic cells precludes simultaneous transcription and translation.
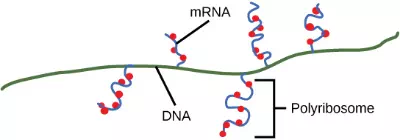
Figure 9.17 Multiple polymerases can transcribe a single bacterial gene while numerous ribosomes concurrently translate the mRNA transcripts into polypeptides. In this way, a specific protein can rapidly reach a high concentration in the bacterial cell.