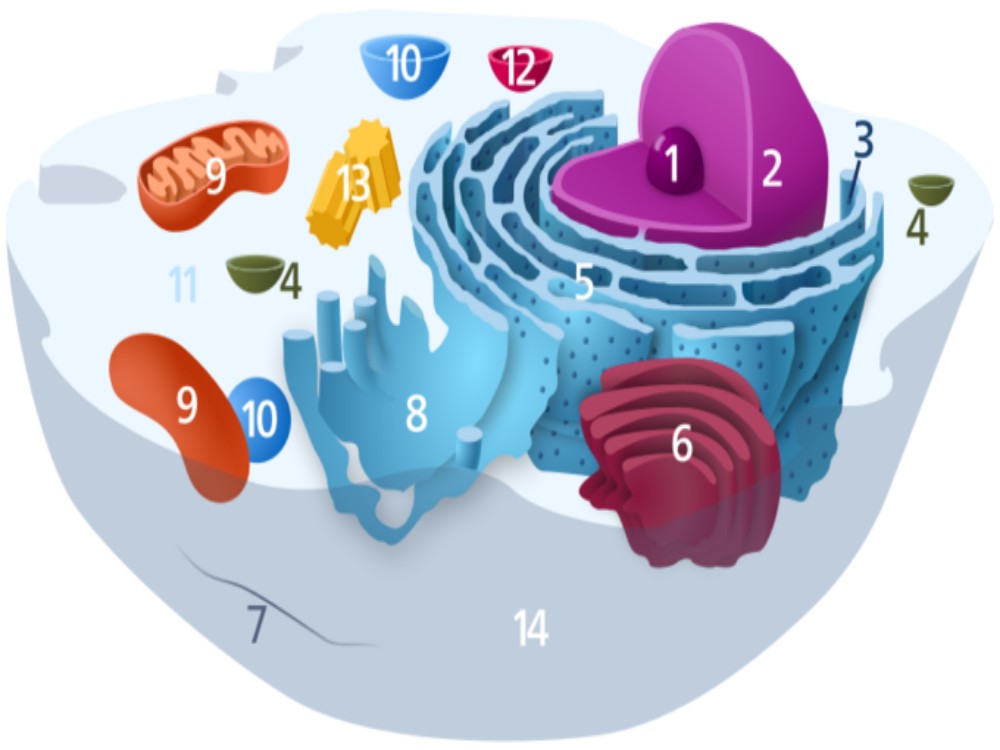
Vesicles and vacuoles are membrane-bound sacs that function in storage and transport. Vacuoles are somewhat larger than vesicles, and the membrane of a vacuole does not fuse with the membranes of other cellular components. Vesicles can fuse with other membranes within the cell system. Additionally, enzymes within plant vacuoles can break down macromolecules.
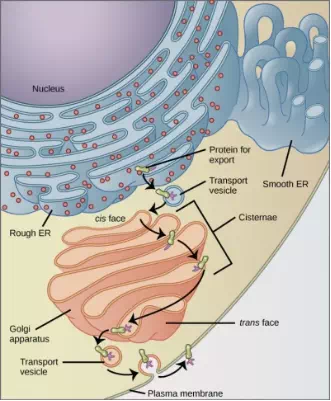
Figure 3.16 The endomembrane system works to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. (credit: modification of work by Magnus Manske)
Why does the cis face of the Golgi not face the plasma membrane?
<!– Because that face receives chemicals from the ER, which is toward the center of the cell. –>