Although the immune system is characterized by circulating cells throughout the body, the regulation, maturation, and intercommunication of immune factors occur at specific sites. The blood circulates immune cells, proteins, and other factors through the body. Approximately 0.1 percent of all cells in the blood are leukocytes, which encompass monocytes (the precursor of macrophages) and lymphocytes. The majority of cells in the blood are erythrocytes (red blood cells). Lymph is a watery fluid that bathes tissues and organs with protective white blood cells and does not contain erythrocytes. Cells of the immune system can travel between the distinct lymphatic and blood circulatory systems, which are separated by interstitial space, by a process called extravasation (passing through to surrounding tissue).
The cells of the immune system originate from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. Cytokines stimulate these stem cells to differentiate into immune cells. B cell maturation occurs in the bone marrow, whereas naïve T cells transit from the bone marrow to the thymus for maturation. In the thymus, immature T cells that express TCRs complementary to self-antigens are destroyed. This process helps prevent autoimmune responses.
On maturation, T and B lymphocytes circulate to various destinations. Lymph nodes scattered throughout the body, as illustrated in Figure 23.20, house large populations of T and B cells, dendritic cells, and macrophages. Lymph gathers antigens as it drains from tissues. These antigens then are filtered through lymph nodes before the lymph is returned to circulation. APCs in the lymph nodes capture and process antigens and inform nearby lymphocytes about potential pathogens.
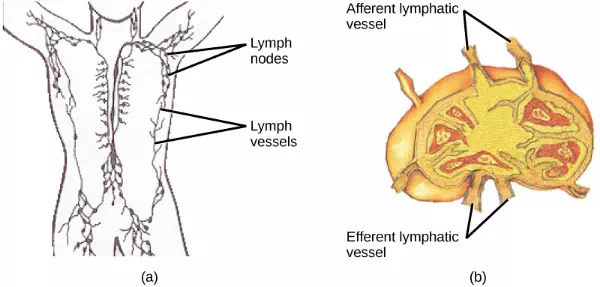
Figure 23.20. (a) Lymphatic vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph throughout the body. The liquid enters (b) lymph nodes through afferent vessels. Lymph nodes are filled with lymphocytes that purge infecting cells. The lymph then exits through efferent vessels. (credit: modification of work by NIH, NCI)
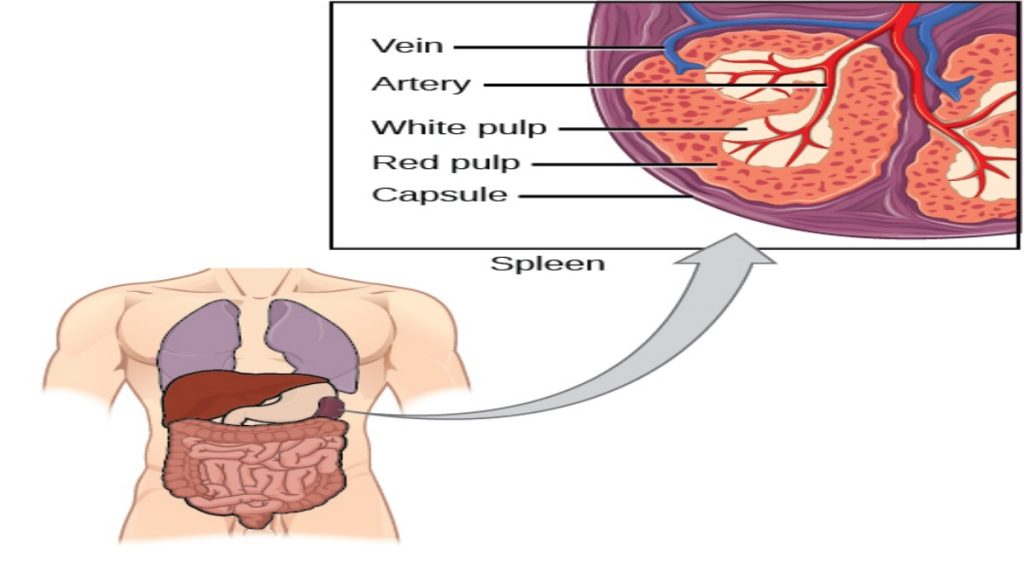
The spleen houses B and T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, and NK cells. The spleen, shown in Figure 23.21, is the site where APCs that have trapped foreign particles in the blood can communicate with lymphocytes. Antibodies are synthesized and secreted by activated plasma cells in the spleen, and the spleen filters foreign substances and antibody-complexed pathogens from the blood. Functionally, the spleen is to the blood as lymph nodes are to the lymph.
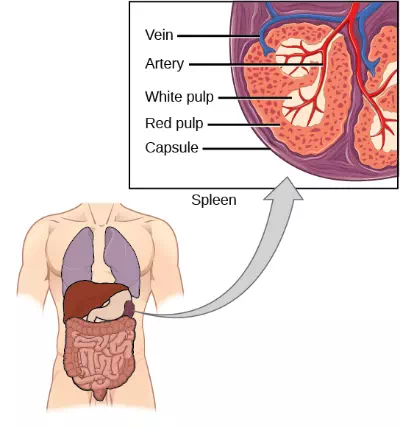
Figure 23.21. The spleen is similar to a lymph node but is much larger and filters blood instead of lymph. Blood enters the spleen through arteries and exits through veins. The spleen contains two types of tissue: red pulp and white pulp. Red pulp consists of cavities that store blood. Within the red pulp, damaged red blood cells are removed and replaced by new ones. White pulp is rich in lymphocytes that remove antigen-coated bacteria from the blood. (credit: modification of work by NCI)
Summary
The adaptive immune response is a slower-acting, longer-lasting, and more specific response than the innate response. However, the adaptive response requires information from the innate immune system to function. APCs display antigens via MHC molecules to complementary naïve T cells. In response, the T cells differentiate and proliferate, becoming TH cells or CTLs. TH cells stimulate B cells that have engulfed and presented pathogen-derived antigens. B cells differentiate into plasma cells that secrete antibodies, whereas CTLs induce apoptosis in intracellularly infected or cancerous cells. Memory cells persist after a primary exposure to a pathogen. If re-exposure occurs, memory cells differentiate into effector cells without input from the innate immune system. The mucosal immune system is largely independent from the systemic immune system but functions in a parallel fashion to protect the extensive mucosal surfaces of the body.