Vertebrates have evolved more complex digestive systems to adapt to their dietary needs. Some animals have a single stomach, while others have multi-chambered stomachs. Birds have developed a digestive system adapted to eating unmasticated food.
Monogastric: Single-chambered Stomach
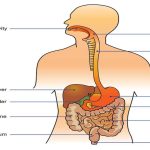
As the word monogastric suggests, this type of digestive system consists of one (“mono”) stomach chamber (“gastric”). Humans and many animals have a monogastric digestive system as illustrated in Figure 15.6 ab. The process of digestion begins with the mouth and the intake of food. The teeth play an important role in masticating (chewing) or physically breaking down food into smaller particles. The enzymes present in saliva also begin to chemically break down food. The esophagus is a long tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Using peristalsis, or wave-like smooth muscle contractions, the muscles of the esophagus push the food towards the stomach. In order to speed up the actions of enzymes in the stomach, the stomach is an extremely acidic environment, with a pH between 1.5 and 2.5. The gastric juices, which include enzymes in the stomach, act on the food particles and continue the process of digestion. Further breakdown of food takes place in the small intestine where enzymes produced by the liver, the small intestine, and the pancreas continue the process of digestion. The nutrients are absorbed into the blood stream across the epithelial cells lining the walls of the small intestines. The waste material travels on to the large intestine where water is absorbed and the drier waste material is compacted into feces; it is stored until it is excreted through the rectum.
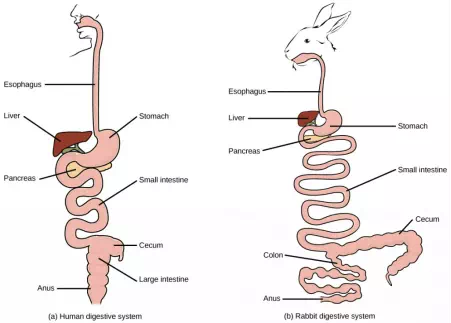
Figure 15.6.
(a) Humans and herbivores, such as the (b) rabbit, have a monogastric digestive system. However, in the rabbit the small intestine and cecum are enlarged to allow more time to digest plant material. The enlarged organ provides more surface area for absorption of nutrients. Rabbits digest their food twice: the first time food passes through the digestive system, it collects in the cecum, and then it passes as soft feces called cecotrophes. The rabbit re-ingests these cecotrophes to further digest them.
Avian
Birds face special challenges when it comes to obtaining nutrition from food. They do not have teeth and so their digestive system, shown in Figure 15.7, must be able to process un-masticated food. Birds have evolved a variety of beak types that reflect the vast variety in their diet, ranging from seeds and insects to fruits and nuts. Because most birds fly, their metabolic rates are high in order to efficiently process food and keep their body weight low. The stomach of birds has two chambers: the proventriculus, where gastric juices are produced to digest the food before it enters the stomach, and the gizzard, where the food is stored, soaked, and mechanically ground. The undigested material forms food pellets that are sometimes regurgitated. Most of the chemical digestion and absorption happens in the intestine and the waste is excreted through the cloaca.
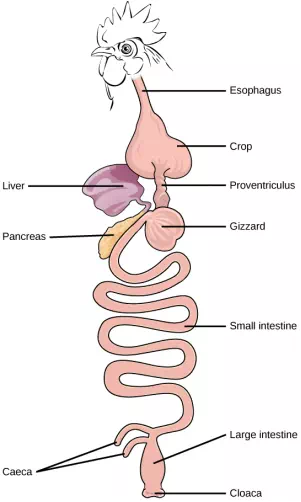
Figure 15.7. The avian esophagus has a pouch, called a crop, which stores food. Food passes from the crop to the first of two stomachs, called the proventriculus, which contains digestive juices that break down food. From the proventriculus, the food enters the second stomach, called the gizzard, which grinds food. Some birds swallow stones or grit, which are stored in the gizzard, to aid the grinding process. Birds do not have separate openings to excrete urine and feces. Instead, uric acid from the kidneys is secreted into the large intestine and combined with waste from the digestive process. This waste is excreted through an opening called the cloaca.
Comments are closed